Homeowner Shocked By First Solar Bill: What Really Happened?
Imagine this: you’ve just installed solar panels, thinking it’s the ultimate step toward energy independence. You’re ready to save money and help the planet. But then, BAM! Your first solar bill lands on your lap, and it’s way higher than you expected. Shocking, right? This is exactly what happened to thousands of homeowners across the U.S., and it’s becoming a common story. If you’re one of them, don’t worry—you’re not alone. Let’s break it down together.
Homeowners often dive into solar energy with high hopes, only to find themselves blindsided by unexpected costs. The truth is, solar energy can be a game-changer, but there’s a lot more to it than just sticking panels on your roof. Understanding how solar billing works and what factors contribute to those costs is key to avoiding surprises down the road.
In this article, we’ll dig deep into why some homeowners get shocked by their first solar bill, how solar energy billing works, and most importantly, how you can prepare for it. So, buckle up and let’s unravel the mystery behind your solar bill!
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Solar Surprise
- How Solar Energy Works for Homeowners
- Breaking Down Your Solar Bill
- Why Homeowners Get Shocked
- Net Metering: Your Secret Weapon
- Time-of-Use Rates: The Hidden Factor
- Understanding Solar Panel Costs
- Tax Credits and Incentives
- Tips to Avoid Billing Surprises
- The Future of Solar Energy
Introduction: The Solar Surprise
So, here’s the deal: switching to solar sounds awesome, right? You’re saving the environment, reducing your carbon footprint, and potentially cutting down on electricity bills. But when that first solar bill comes in, some people are left scratching their heads. Like, "Wait… wasn’t this supposed to save me money?"
It’s a reality check that many homeowners face after installing solar panels. While solar energy is an incredible investment, it’s not as simple as flipping a switch and forgetting about it. There are nuances to how solar energy works, especially when it comes to billing. Let’s dive into the basics first.
How Solar Energy Works for Homeowners
Let’s start with the basics. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which powers your home. Any excess energy your panels produce is sent back to the grid, and you earn credits for it. This process is called net metering, and it’s like a bank account for your energy usage. When you need more energy than your panels can produce—like during cloudy days or nighttime—you draw from the grid and use those credits.
Here’s the thing, though: the amount of energy your panels produce depends on several factors, including:
- The size and efficiency of your solar system
- Your geographic location and climate
- Your home’s orientation and roof angle
- Shading from trees or other structures
So, while solar panels can significantly reduce your energy costs, they don’t always eliminate them entirely. That’s why understanding how the system works is crucial.
Why Solar Energy is a Smart Move
Solar energy isn’t just about saving money. It’s also about sustainability and independence. By generating your own electricity, you’re less reliant on traditional power sources, which are often tied to volatile energy prices. Plus, solar systems have a long lifespan, often lasting 25 years or more with minimal maintenance. That’s a solid investment for any homeowner.
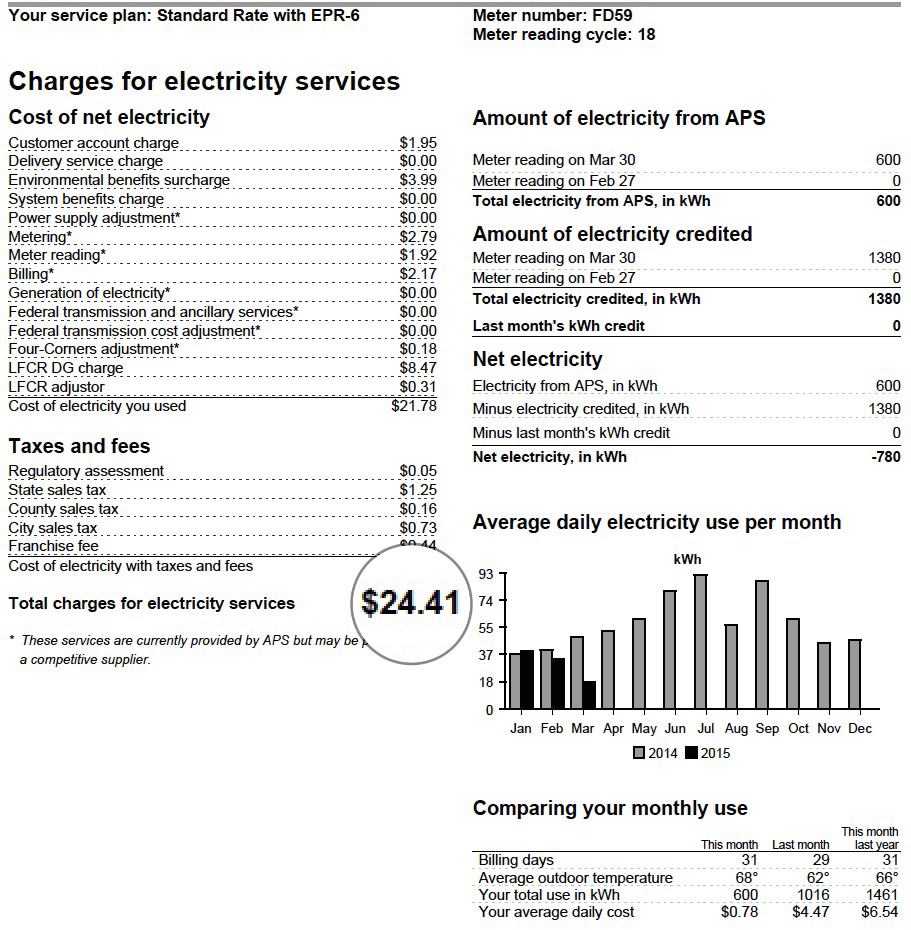
Breaking Down Your Solar Bill
Now, let’s talk about the elephant in the room: your solar bill. What exactly is it made up of? Your solar bill typically includes two main components:
- Electricity usage: This is the energy you pull from the grid when your panels aren’t producing enough.
- Fixed charges: These are fees your utility company charges for maintaining the grid infrastructure, regardless of how much energy you use.
Here’s where things can get tricky. Even if your solar panels produce most of the energy you need, you might still see charges on your bill. Why? Because you’re still connected to the grid, and utility companies charge for that connection.
What to Look For in Your Bill
When you receive your solar bill, pay attention to these key sections:
- Net energy usage: This shows the difference between the energy you produce and the energy you consume.
- Net metering credits: These are the credits you earn for sending excess energy back to the grid.
- Time-of-use rates: Some utility companies charge different rates depending on when you use energy.
Understanding these components can help you make sense of your bill and avoid unnecessary surprises.
Why Homeowners Get Shocked
Okay, so why do some homeowners get so shocked by their first solar bill? There are a few common reasons:
- Misunderstanding net metering: Some homeowners assume they won’t have to pay anything once they go solar. But as we’ve seen, that’s not always the case.
- Time-of-use rates: If your utility company charges higher rates during peak hours, your bill could end up being higher than expected.
- Fixed charges: These fees can add up, especially if you’re not aware of them.
- Underestimating energy needs: If your solar system isn’t sized correctly for your energy consumption, you might end up pulling more energy from the grid than anticipated.
It’s important to have realistic expectations about what solar energy can and can’t do for your wallet.
Net Metering: Your Secret Weapon
Net metering is one of the best features of going solar. It allows you to earn credits for the excess energy your panels produce and use those credits when you need them. Think of it as a way to balance your energy usage over time.
However, not all states offer net metering, and the rules can vary widely. Some states cap the amount of credits you can earn, while others allow you to roll over unused credits indefinitely. Knowing the specifics of your state’s net metering policy is essential for maximizing your savings.
How Net Metering Works
Here’s a quick breakdown of how net metering works:
- Your solar panels produce energy during the day.
- Any excess energy is sent back to the grid, and you earn credits for it.
- When your panels aren’t producing enough energy, you draw from the grid and use those credits.
It’s like having a personal energy bank that helps you manage your usage more efficiently.
Time-of-Use Rates: The Hidden Factor
Time-of-use (TOU) rates are another factor that can affect your solar bill. Many utility companies charge different rates depending on when you use energy. Peak hours, usually in the evening, often come with higher rates, while off-peak hours, like late at night, have lower rates.
If your solar panels don’t produce enough energy during peak hours, you might end up paying more than you expected. That’s why it’s important to understand your utility company’s TOU policy and plan your energy usage accordingly.
Managing TOU Rates
Here are a few tips to help you manage TOU rates:
- Shift energy-intensive tasks, like laundry or dishwashing, to off-peak hours.
- Invest in a battery storage system to store excess energy produced during the day for use during peak hours.
- Monitor your energy usage closely to identify patterns and adjust accordingly.
By being strategic about when and how you use energy, you can minimize the impact of TOU rates on your bill.
Understanding Solar Panel Costs
While solar panels can save you money in the long run, the upfront costs can be significant. The average cost of a residential solar system ranges from $15,000 to $25,000 before incentives. However, there are several ways to reduce these costs:
- Federal tax credit: The federal government offers a tax credit of up to 30% of the system’s cost.
- State incentives: Many states offer additional incentives, such as rebates or grants.
- Financing options: Some companies offer low-interest loans or leases to make solar more affordable.
When calculating the return on investment (ROI) of your solar system, consider both the upfront costs and the long-term savings.
Tax Credits and Incentives
Tax credits and incentives are a huge part of making solar energy more accessible to homeowners. The federal solar tax credit, also known as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), allows you to deduct a percentage of your solar system’s cost from your federal taxes. This credit is set to decrease over time, so it’s worth taking advantage of it sooner rather than later.
In addition to federal incentives, many states and local governments offer their own programs to encourage solar adoption. These can include rebates, grants, and property tax exemptions. Doing your research and taking advantage of these programs can significantly reduce the cost of going solar.
How to Claim Your Tax Credit
Claiming your solar tax credit is relatively straightforward. Here’s what you need to do:
- Keep all your receipts and documentation related to your solar installation.
- File Form 5695 with your federal tax return.
- Consult with a tax professional if you’re unsure about how to claim the credit.
By taking advantage of these incentives, you can make solar energy a more affordable option for your home.
Tips to Avoid Billing Surprises
Now that we’ve covered the basics, here are some tips to help you avoid billing surprises:
- Understand your utility company’s policies: Make sure you know how net metering, TOU rates, and fixed charges work in your area.
- Monitor your energy usage: Keep an eye on how much energy your panels produce and how much you consume.
- Consider battery storage: A battery system can help you store excess energy and reduce reliance on the grid.
- Plan for seasonal variations: Solar production can fluctuate depending on the weather and time of year.
By staying informed and proactive, you can ensure that your solar investment pays off as expected.
The Future of Solar Energy
As technology continues to advance, the future of solar energy looks bright. Solar panels are becoming more efficient, battery storage systems are getting cheaper, and more incentives are being introduced to encourage adoption. In the coming years, we can expect solar energy to play an even bigger role in powering homes and businesses around the world.
For homeowners, this means more opportunities to save money and reduce their carbon footprint. Whether you’re just starting to consider solar or already have a system installed, staying informed about the latest developments can help you make the most of your investment.
What’s Next for Solar?
Here are a few trends to watch for in the solar energy space:
- Increased adoption of smart home technology to optimize energy usage.
- Advancements in battery storage to make solar systems more self-sufficient.
- Expansion of community solar programs to make solar accessible to more people.
As the solar industry continues to evolve, the possibilities are endless.
Conclusion
So, there you have it: the ins and outs of why some homeowners get shocked by their first solar bill. While solar energy is an incredible investment, it’s important to understand how it works and what factors can affect your costs. By staying informed